You might think a bruise is just a minor inconvenience, but a contusion injury can be more complex than it appears. When you experience one, it’s not just your skin that changes color; there’s a whole process happening beneath the surface. Each stage tells a story about your body’s healing process, from the initial reddish mark to the final yellow hue. Have you ever wondered why some bruises hurt more than others or linger for weeks? Exploring the intricacies of contusions reveals much about your body’s resilience and potential underlying concerns. What’s the next step in understanding these common yet intriguing injuries?
Key Takeaways
- Contusions are caused by blunt force trauma, leading to bruising, swelling, and pain.
- Types include muscle, bone, brain, and lung contusions with varying symptoms and healing times.
- The RICE protocol (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) is crucial for managing contusions initially.
- Diagnosis may require imaging tests to assess severity and rule out fractures or other injuries.
- Prevention includes proper warm-up, protective gear, and strength training to reduce injury risk.
Understanding Contusions
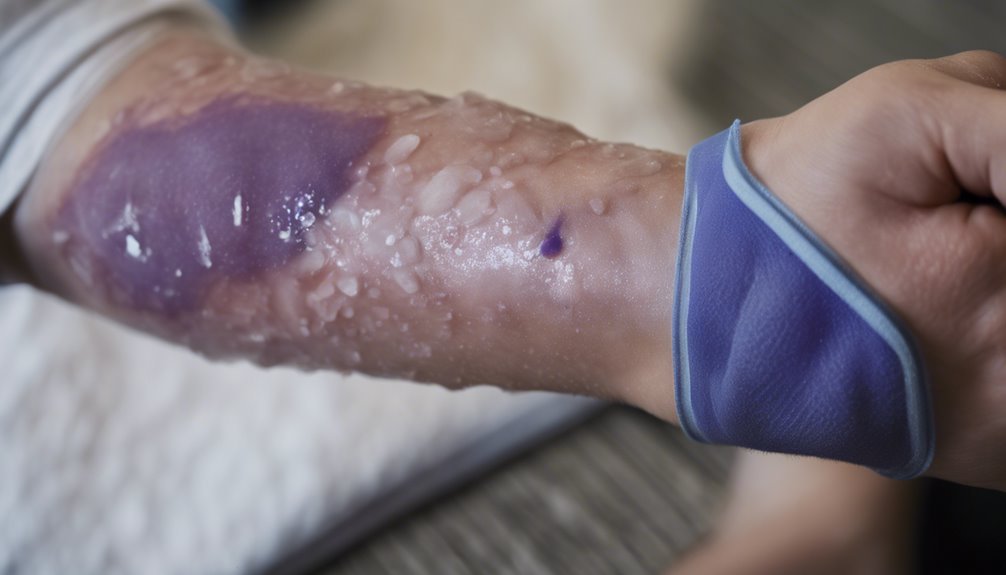
A contusion often catches you off guard, leaving a telltale bruise. This injury occurs when a direct impact breaks small blood vessels under the skin, resulting in swelling and discoloration.
Contusions aren’t just skin-deep; they can also affect muscles and other soft tissues, making them more painful and sometimes more severe. Muscle contusions, in particular, cause significant discomfort and may require more attention than a simple skin bruise.
Understanding the symptoms is essential for effective management. You’ll notice localized pain, swelling, and stiffness. The color of the bruise can start red, shift to purple, and eventually fade to yellow as it heals.
To address these symptoms, you should follow the RICE protocol. Rest the injured area, apply Ice to reduce swelling, use Compression to support the soft tissues, and Elevate the injury to minimize blood flow and swelling.
In more severe cases, seeking medical care is critical. A healthcare professional might perform a physical examination or request imaging tests like an MRI or ultrasound to evaluate the damage and rule out fractures.
This guarantees you receive the proper recovery treatment.
Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a contusion is key to managing the injury effectively. One of the most noticeable symptoms is skin discoloration, often starting as red or purple bruising. As the bruise heals, it might turn yellow.
Another common symptom is swelling. It occurs when fluid and blood from broken capillaries accumulate around the affected area. This swelling can cause tightness and stiffness in the muscles and joints nearby, making movement painful or challenging.
Pain is a significant symptom that varies based on the contusion’s severity. You might find that the pain intensifies with pressure or when you try to move the affected area. In more severe cases, a hematoma can develop. This is a localized swelling filled with blood, forming a noticeable lump.
It’s important to pay attention to these symptoms. If you notice stiffness or difficulty moving, it might be due to swelling or a hematoma. Monitoring these signs can help you determine the best course of action for recovery, whether it’s resting the area, applying ice, or seeking medical attention for severe contusions.
Types of Contusions
Contusions can vary considerably depending on their location and severity, each presenting unique challenges and symptoms. Muscle contusions often occur in contact sports like football, where blunt force trauma bruises the muscle fibers but leaves the skin intact. You’ll notice contusion symptoms such as pain, inflammation, and swelling. Bone contusions, on the other hand, result from high-impact activities. They cause bleeding within the bone tissue and present as localized tenderness. These injuries generally take longer to heal than muscle contusions.
Here’s a quick reference to understand different types of contusions:
| Type of Contusion | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Muscle Contusion | Blunt trauma in muscles; pain, swelling; common in sports |
| Bone Contusion | High-impact injury; bleeding in bone; tenderness |
| Brain Contusion | Head impact; bruised brain tissue; possible function loss |
| Lung Contusion | Chest trauma; bruised lung; no tissue tear |
For mild contusions, NSAIDs can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. However, healing time can vary, requiring patience and, sometimes, medical intervention. Understanding the specific type of traumatic injury you’re dealing with helps you determine the best course of treatment and recovery strategy.
Causes of Contusions
How do contusions typically occur? They often result from a direct blow or blunt force trauma to your body. This can happen during everyday accidents like falls or slips and is common in motor vehicle collisions. Such incidents cause damage to your blood vessels under the skin, leading to the characteristic bruising associated with contusions.
You’re at a higher risk for muscle contusions if you’re active in contact sports. Football, rugby, or hockey involve high-impact activities where collisions and tackles are commonplace. These sports-related injuries happen because intense physical contact can lead to muscle contusions from the repeated blows your body might endure.
Athletes, however, can also experience contusions from overuse injuries. Engaging in strenuous activities without giving your body enough time to recover can stress your muscles and blood vessels, making them more susceptible to bruising without a direct impact.
Certain medical conditions that weaken blood vessel integrity can also increase your vulnerability to contusions. Bleeding disorders, for instance, can make your blood vessels more fragile, meaning even minor bumps or pressure might lead to noticeable bruising.
Understanding these causes helps in preventing and managing contusions effectively.
Diagnosis and Testing
Understanding the causes of contusions can help in anticipating possible injuries, but proper diagnosis and testing guarantee effective treatment and recovery. A physical examination is your first step in diagnosing contusions. It assesses the injury’s location, severity, and nature by checking for pain, swelling, and visible bruising. Your medical history provides valuable context, helping doctors understand the trauma mechanism and associated symptoms for accurate diagnosis.
For a clearer picture, imaging tests like X-rays are used to rule out fractures, but MRI scans are your go-to for viewing soft tissue injuries and internal bleeding. If you’re dealing with cerebral or spinal contusions, neurological evaluations are vital. These tests assess cognitive function, motor skills, and potential nerve damage to confirm no underlying issues are missed.
Follow-up examinations are important, especially if symptoms persist or worsen. These might indicate complications that require further medical intervention.
Here’s a quick overview:
| Diagnostic Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Physical Examination | Assess injury location and severity |
| Medical History | Contextual understanding of trauma |
| Imaging Tests | Rule out fractures with X-rays |
| MRI Scans | Visualize soft tissue and internal bleeding |
| Neurological Evaluations | Assess cognitive and motor functions |
Treatment Options
Treating contusions effectively starts with the tried-and-true R.I.C.E. method—Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
First, rest the injured area to prevent further damage to the muscle fibers. Then, apply ice for 15-20 minutes several times daily to reduce swelling and relieve pain. Make certain to wrap the ice in a cloth to protect your skin.
Compression is another key component; a compression wrap or bandage can help manage swelling and support the injured area, promoting better healing.
Additionally, NSAIDs like ibuprofen can be a valuable part of your treatment plan. These medications reduce inflammation and help alleviate pain, making it easier for you to manage daily activities. However, always follow the dosage instructions or consult your healthcare provider to guarantee safe use.
If your symptoms persist or worsen, don’t hesitate to seek medical attention. A healthcare provider can assess your condition and, if necessary, recommend imaging tests to rule out more severe injuries.
Taking these steps guarantees that your contusion receives the best possible care, promoting a quicker and more effective recovery.
Prevention and Recovery
Always start with proper warm-up and cool-down exercises to prevent contusion injuries and wear protective gear during contact sports.
If you get injured, the R.I.C.E. method can help speed up your recovery, but monitor your symptoms closely.
Understanding the risk factors, such as cluttered spaces and sudden activity increases, can further protect you from future contusions.
Effective Injury Prevention Tips
Preventing contusion injuries requires a proactive approach to both preparation and safety measures. Start by engaging in a proper warm-up before any physical activities. This routine helps prepare your muscles, reducing the risk of muscle contusions.
Don’t overlook the importance of protective gear, especially if you play contact sports. Gear like pads and helmets are essential for injury prevention by protecting against blunt force trauma.
Incorporate strength training and flexibility exercises into your fitness regimen. These activities enhance muscle resilience and flexibility, making your body less susceptible to injuries.
Also, gradually increase the intensity of your workouts. This gradual progression allows your muscles and tissues to adapt, minimizing the risk of overuse injuries, including recurrent contusions.
Additionally, guarantee your environment is safe and clutter-free. This is crucial to prevent falls, a common cause of contusions, especially if you have young children or elderly family members at home.
By taking these steps, you can markedly lower the risk of contusion injuries and enjoy your physical activities confidently and safely.
Accelerated Healing Strategies
To recover swiftly from a contusion, start by applying the R.I.C.E. method—rest, ice, compression, and elevation—immediately after the injury. This approach considerably reduces swelling and sets the stage for faster healing within the first 48 hours.
Focus on your diet to support tissue repair and recovery. Consuming foods high in protein, vitamin C, and zinc boosts collagen synthesis and strengthens your immune system, which is vital for healing outcomes.
Once initial inflammation decreases, gentle physical therapy exercises can restore your range of motion and prevent stiffness. These activities are necessary for quicker rehabilitation and ensuring you regain full function.
Don’t underestimate the power of staying hydrated. Proper fluid intake improves circulation and enhances nutrient delivery to the injured area, further accelerating the healing process.
Moreover, steer clear of alcohol and smoking during your recovery. These substances hinder circulation and can delay tissue repair, negatively affecting healing outcomes.
Risk Factors Awareness
Understanding risk factors is essential for both preventing and recovering from contusion injuries. If you’re involved in contact sports, you’re at a higher risk of experiencing contusions due to frequent collisions that can cause blunt-force trauma. It’s vital to recognize these risk factors and take preventive measures.
Wearing protective gear during physical activities can greatly minimize the chances of injury. If you’re over 65, be aware that falls are more likely due to decreased bone density and balance, making you more susceptible to contusions.
For those with bleeding disorders or on anticoagulant medications, even minor impacts can lead to considerable bruising. Understanding your condition’s implications on contusion recovery is important in such cases.
Keeping your environment clutter-free can also help prevent falls, reducing contusion risks.
Incorporating proper warm-up routines before engaging in physical activities can prevent muscle overuse and reduce injury risks. Gradually increasing the intensity of your activities helps your body adapt, reducing the likelihood of contusions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do You Treat a Contusion?
Treat a contusion by prioritizing rest and recovery. Use ice application and compression techniques to reduce swelling. Elevation methods help, too. Incorporate stretching exercises and massage therapy in rehabilitation exercises. Implement prevention strategies for future injuries.
Is a Contusion a Serious Injury?
You might wonder if a contusion is serious. It depends on the cause, symptoms, and complications. Proper diagnosis and prevention are essential. Athletes often experience contusions, so it is important to understand their recovery and differentiate them from bruises.
How Long Does a Muscle Contusion Take to Heal?
Healing time varies; mild contusions heal in days, and severe ones take weeks to months. Focus on muscle recovery time through rehabilitation exercises. Cold therapy is effective, uses compression bandaging, and employs contusion prevention strategies for sports-related injuries, avoiding long-term effects.
What Pain Medication Is Good for Contusions?
You can manage pain with over-the-counter options like NSAIDs or acetaminophen. As home remedies, try applying ice and topical treatments. Follow dosage recommendations and consult a doctor for prescription medications and additional recovery tips if needed.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of contusion injuries early on is important. By understanding the different types and causes, you can take proactive steps to manage them. Remember, the RICE protocol is your go-to for immediate relief. Don’t hesitate to seek medical evaluation if severe symptoms arise. Preventing future contusions through protective measures and proper care will speed up recovery. Stay informed and attentive to guarantee your body’s healing process is smooth and effective.