You might be surprised at how much a simple image can reveal about a partially torn bicep. These pictures aren’t just for shock value; they offer vital insights that can influence your treatment journey. Imagine being able to pinpoint exactly where the injury is and how severe it might be—all from a visual assessment. This kind of clarity can be essential in deciding whether you need rest, physical therapy, or perhaps something more intensive. But how exactly do these images guide your path to recovery? That’s where the conversation truly begins.
Key Takeaways
- Partially torn bicep pictures often show swelling and bruising around the affected area.
- Images may depict a noticeable gap or indentation in the bicep muscle.
- Diagnostic images like ultrasounds and MRIs reveal details of the tendon tear.
- Visuals can help identify the severity and location of the bicep tear.
- Comparing images of healthy and injured biceps clarifies differences due to partial tears.
Understanding Bicep Anatomy
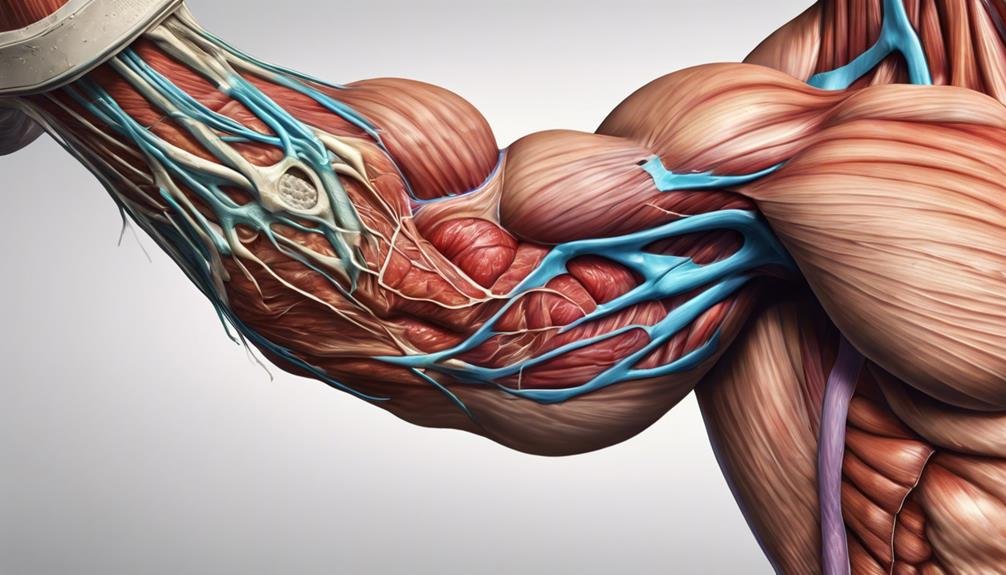
Understanding the anatomy of the bicep is pivotal when dealing with injuries such as partial tears. The bicep muscle, consisting of two heads—the long head and the short head—plays a critical role in arm movement. These two heads connect to the shoulder and elbow via tendons. When working properly, the bicep tendon allows you to flex your elbow and rotate your forearm, essential for everyday tasks.
However, injuries to this tendon can lead to partial tears, directly impacting the function and strength of your arm.
If you experience a partially torn bicep tendon, you’ll likely notice pain, weakness, and a limited range of motion. These symptoms can make even simple actions challenging, affecting your daily life. Understanding the anatomy of your bicep helps in diagnosing and treating these partial tears.
Knowing the specific roles of each bicep head and how they connect to your shoulder and elbow allows for more effective recovery strategies, ensuring your arm regains its full strength and range of motion. By appreciating the intricate design of the bicep, you can better address injuries and support healing.
Causes of Bicep Tears
Bicep tears often result from sudden injuries, like lifting heavy objects or experiencing a sudden impact. When you’re involved in activities requiring heavy lifting, your bicep tendon can undergo immense stress. This stress sometimes leads to a tendon tear, particularly if your lifting technique is poor.
A severe form of this injury is the distal biceps tendon rupture, where the tendon detaches near the elbow, causing significant pain and requiring careful treatment.
Over time, repetitive motions can also wear down your bicep tendon. Whether you’re engaged in sports or everyday tasks, the constant strain can inflame the tendon, ultimately leading to a tear. It’s essential to recognize how age-related degeneration plays a role, too. As you age, your tendons naturally weaken, making them more susceptible to damage. This weakening increases the likelihood of experiencing a bicep tear, particularly if you’re active in sports like weightlifting or contact sports.
Preventing these tears involves more than just avoiding heavy lifting. You need to focus on proper form to minimize stress on the bone and surrounding structures. Understanding these causes can help you take preventive measures, reducing your risk of enduring the pain and lengthy recovery associated with bicep injuries.
Identifying Tear Symptoms

Spotting the symptoms of a partially torn bicep early can help you seek timely treatment and avoid further injury. If you suspect a tear in your biceps muscle, pay close attention to your upper arm for signs of trouble. One of the most telling symptoms is localized pain and swelling in the area. This discomfort often comes with tenderness, making it uncomfortable to touch or move the arm.
Partial tears can also lead to weakness in the affected arm, especially noticeable during activities that require engaging the biceps muscle, like lifting or pulling. You might find it difficult to perform tasks you previously managed with ease.
Another symptom to watch for is a limited range of motion; you may struggle to fully extend or flex your arm as you could before the injury.
Don’t overlook visible bruising or discoloration around the bicep area, as this can also indicate a partial tear. Additionally, some people experience a popping sensation or snapping feeling during arm movements, which might be unsettling.
Recognizing these symptoms promptly allows you to address the issue before it worsens, preventing potential long-term complications.
Diagnostic Imaging Techniques
Once you’ve identified the symptoms of a partially torn bicep, seeking a proper diagnosis is the next step. Diagnostic imaging techniques play a pivotal role in this process.
Ultrasound is often the first choice for diagnosing soft tissue injuries, such as partial bicep tears, because it provides real-time evaluation. It allows doctors to see the injury’s extent and make a preliminary assessment.
For a more detailed view, an MRI scan is invaluable. It offers clear images of muscle and tendon injuries, ensuring an accurate diagnosis of your partially torn biceps. This helps in understanding the exact nature of the tear, which is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.
X-rays, on the other hand, aren’t typically used to visualize soft tissue injuries directly. However, they’re instrumental in ruling out any bone-related issues or abnormalities that may accompany a partially torn bicep. By eliminating other potential problems, X-rays contribute to a thorough assessment.
Combining these imaging modalities gives healthcare providers a complete picture of the injury. This combination assists in determining the location, size, and severity of the tear, which is essential for precise treatment planning.
Treatment and Rehabilitation
Your recovery journey after experiencing a partially torn bicep starts with understanding the treatment and rehabilitation process. Initially, you might use the RICE method to manage inflammation and pain. For a distal biceps tendon tear, surgical treatment may be necessary, especially if there’s a significant decrease in strength or risk of complete tears. Whether or not surgery is involved, physical therapy plays a pivotal role in your recovery. It helps restore strength and flexibility, allowing you to gradually return to daily activities.
To protect the repair and avoid re-injury, immobilization with a splint or brace might be needed. As your recovery progresses, you’ll need to focus on specific exercises. These exercises are essential for:
- Strengthening the bicep muscle
- Improving flexibility and function
- Safely resuming overhead activities
A gradual progression of exercises is vital to prevent further tendon tears. Your physical therapist will carefully monitor your progress, adjusting the rehabilitation plan as needed based on your individual response and recovery. Remember, every step is important to restore your strength fully and get back to your routine activities safely.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Know if I Partially Tore My Bicep?
You might have a partially torn bicep if you experience bicep pain, swelling signs, or weakness. Check a symptoms checklist, get an MRI diagnosis, and explore treatment options like physical therapy. Understand risk factors and focus on preventing re-injury.
Can a partial bicep tear heal itself?
Yes, a partial bicep tear can heal naturally. Use rest and ice, engage in physical therapy, and include strengthening exercises in your rehabilitation process. Focus on pain management, avoid aggravation, and guarantee a gradual return to activities.
Can You Move Your Arm With a Torn Bicep?
You can move your arm with a torn bicep but expect limited arm mobility and varying pain levels. Physical therapy and exercise modifications improve muscle strength and range of motion. Treatment options also address swelling symptoms and recovery time.
Do I Need Surgery for a Partial Distal Bicep Tear?
You don’t always need surgery for a partial distal bicep tear. Consider recovery options like non-surgical treatments, physical therapy, and alternative therapies. Focus on pain management, preventing future injuries, and understanding the rehabilitation process and long-term effects.
Conclusion
To sum up, understanding your bicep’s anatomy and the causes of tears can help you recognize symptoms early on. With diagnostic imaging techniques, you’ll get a clearer picture of the injury, aiding healthcare professionals in crafting an effective treatment plan. Whether it’s rest, physical therapy, or surgery, knowing the extent of your tear is essential. By actively engaging in your recovery process, you’ll be better equipped to manage your rehabilitation journey and achieve a successful recovery.